Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women, and hormone treatment is used to treat it. Breast cancer can be detected in its early stages with mammograms. Perhaps before it has made any progress. Use the links on this page to learn more about breast cancer prevention, screening, treatment, statistics, research, and clinical trials, among other things.
Breast cancer is a disease that causes malignant (cancer) cells to develop in the breast tissues.
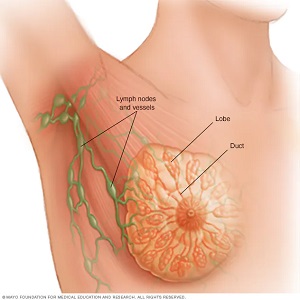
The breast is made up of lobes and ducts
Each breast has anything from fifteen to twenty lobes. Each lobe is made up of several lobules. A slew of milk-producing bulbs forms the lobules’ apex. Ducts are thin tubes that connect the lobes, lobules, and bulbs.
Blood and lymph vessels can be seen in both breasts. Lymph is a clear, virtually colourless fluid that travels through vessels. Lymph veins are in charge of transporting lymph between lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes in the shape of beans are found throughout the body. They filter lymph and store white blood cells, which help the body fight illness and infection. Lymph nodes can be found in the axilla (under the arm), above the collarbone, and around the breast in the chest.
The most common type of breast cancer is ductal carcinoma, which develops in ductal cells. A type of breast cancer is lobular carcinoma. This type of breast cancer develops in the lobes or lobules and is more commonly diagnosed in both breasts than other types of breast cancer. Inflammatory breast cancer is a type of breast cancer that is distinguished by breast redness, swelling, and warmth to the touch.
Breast cancer can be caused by hereditary gene alterations (changes)
Genes carry the genetic information passed down from parents within cells. Hereditary breast cancer accounts for 5 to 10% of all cases of breast cancer. Certain ethnic groups have a higher prevalence of breast cancer-related genetic abnormalities.
Breast cancer is more common in women who have particular gene mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2. These women are more likely to get ovarian cancer and may also be more likely to develop other cancers. Men who carry a defective gene linked to breast cancer are more likely to develop the disease. Male Breast Cancer Treatment offers further information.
Several gene mutation detection assays are available. These genetic tests are sometimes performed on cancer-prone family members. More information can be found at Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers.
Breast cancer must be diagnosed
If you notice any changes in your breasts, you should see a doctor. Here are some examples of possible testing and processes:
Physical examination and review of medical records: Examining the body for general signs of illness, such as tumours or anything out of the ordinary. A history of previous illnesses and treatments, as well as the patient’s health habits.
CBE (clinical breast examination): A breast examination is carried out by a doctor or another medical professional. The breasts and underarms will be extensively examined for lumps and other abnormalities by the doctor.
A mammogram is a type of breast x-ray.
Cancer Prevention Efforts
Cancer of the breast Any measure taken to lower the probability of developing cancer is referred to as prevention. Cancer prevention lowers the number of new cancer cases in a population or group. This has the potential to reduce cancer incidence and mortality.
Cancer is a group of diseases. Our genes, lifestyle, and environment all have a role in our vulnerability to cancer. The unique combination of these elements determines each individual’s cancer risk.
A cancer risk factor is anything that raises the likelihood of developing cancer, whereas a cancer protective factor is anything that reduces this likelihood.
Few cancer risk factors can be avoided, but the vast majority cannot. For example, both smoking and inheriting specific genes are cancer risk factors, yet only smoking may be avoided. Regular physical activity and a healthy diet may help prevent against certain cancers. Avoiding risk factors and boosting preventive measures lessen your chances of having cancer, but they do not remove the possibility.
A variety of cancer prevention measures are being researched, including changing one’s lifestyle or dietary habits and avoiding recognised carcinogens.
- Taking medication to treat or prevent cancer or precancerous diseases.
- Treatment for early, localised, or surgical breast cancer
- For further information on the treatments discussed, see the Overview of Treatment Options section.
Treatment options for early, limited, or operable breast cancer include the following:
Surgery
Breast-conserving surgery with sentinel lymph node biopsy A lymph node dissection is performed if malignancy is found in the lymph nodes.
alterations to a radical mastectomy Additionally. Breast reconstruction surgery is an option.
Following surgical treatment, radiotherapy is used.
Breast-conserving surgery is recommended for women who have had breast cancer to lower the likelihood of cancer recurrence. get radiation therapy to the whole breast Regional lymph nodes may be treated using radiation therapy.
If any of the following requirements are satisfied, radiation therapy is used to lower the risk of cancer recurrence in women who have had a modified radical mastectomy:
Cancer has been found in at least four lymph nodes.
Cancer had spread to the lymph node tissue around it.
The tumour was enormous
A secondary tumour has formed along the margins of the resected initial tumour.
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone therapy is a breast cancer treatment that inhibits cancer cell proliferation by eliminating or reducing hormone function. Hormones are substances that are produced by glands and circulate in the bloodstream.
Certain hormones can encourage the formation of certain cancers. If tests show that cancer cells have hormone attachment sites (receptors), medicines, surgery, or radiation therapy may be used to reduce hormone synthesis or activity.
The ovaries produce the majority of the hormone oestrogen, which induces the production of some breast tumours. Ablation is a surgical procedure that stops the ovaries from releasing oestrogen.
Some postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer get aromatase inhibitor-based hormone treatment. Breast Cancer Pills lower oestrogen levels by blocking aromatase from converting testosterone to oestrogen. Arimidex 1 mg is an aromatase inhibitor.
I am a professional writer and blogger. I’m researching and writing about innovation, Entertainment, technology, business, and the latest digital marketing trends click here to go website. Follow my blog here & Visit my website here.